South African waters have long been known as a haven for marine wildlife, with the great white shark holding a special place in the hearts of nature enthusiasts and divers. However, recent developments have left conservationists and researchers deeply concerned. The presence of two killer whales, known as Port and Starboard, along with the looming threat of climate change, has resulted in the dwindling population of great white sharks. This not only has far-reaching ecological consequences but also impacts tourism in the area.
The Reign of Port and Starboard
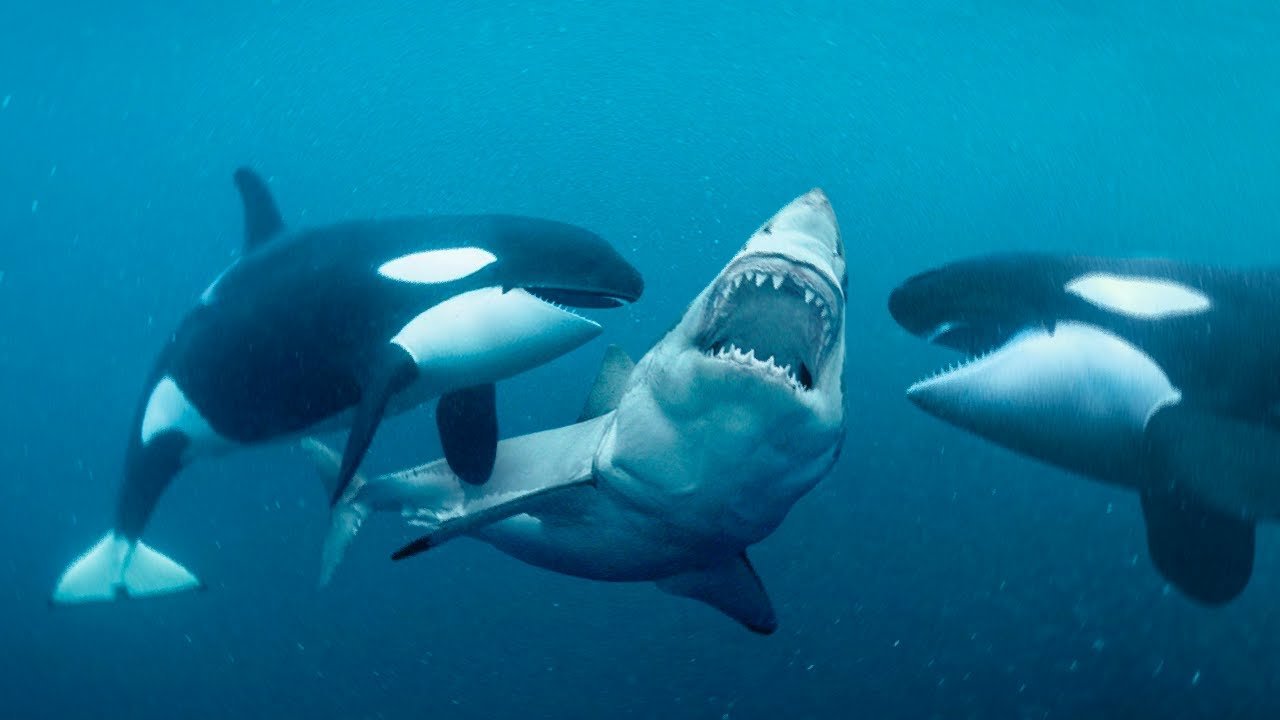
Port and Starboard, two highly intelligent and formidable killer whales, have gained notoriety for their predation on great white sharks. These apex predators possess an extraordinary ability to target and feed on the livers of these sharks, leaving their carcasses to sink to the ocean floor. This alarming phenomenon has significantly impacted the already vulnerable great white shark population in South African waters. Researchers are still unraveling the reasons behind the killer whales' targeting of great whites, but their presence has disrupted the natural balance and led to a decline in shark numbers.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change is another factor that is likely influencing the movements of killer whales and subsequently impacting great white sharks. The warming of oceans alters the distribution and abundance of prey species, causing ripple effects throughout the marine food chain. As global temperatures rise, it is hypothesized that the migration patterns of killer whales may be affected. This could result in a shift in their hunting grounds, including areas where great whites reside, exacerbating the pressure on the already struggling shark population.
The Ripple Effect on Tourism and Local Economy
The decline in great white shark numbers has had a profound impact on tourism in South Africa, particularly in regions like Gansbaai and False Bay, which are renowned for their shark cage diving experiences. Tourists flock to these areas with hopes of encountering these majestic creatures in their natural habitat. However, the scarcity of great whites has left many visitors disappointed and local businesses struggling. The decline in tourism revenue not only affects operators and boat charters but also has a cascading effect on the entire local economy.
Ecological Consequences
The absence of great white sharks in South African waters has broader ecological implications. These sharks play a crucial role as top predators, regulating the marine ecosystem by controlling the populations of prey species. With their declining numbers, there may be a cascading effect on the abundance and behavior of other marine species, disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem. The loss of great whites could lead to an unchecked increase in certain prey species, impacting the overall health and diversity of the marine environment.
Conservation Efforts and the Way Forward
Addressing the challenges faced by great white sharks in South African waters requires collaborative efforts from scientists, conservation organizations, and policymakers. Research into the behavior and movements of killer whales is vital to understand their impact on great white sharks and develop strategies to mitigate this predation. Additionally, studying the potential effects of climate change on the distribution of killer whales can help predict future shifts in their habitat.
To protect the marine ecosystem, it is crucial to establish marine protected areas that safeguard key habitats and ensure the long-term survival of great white sharks. Community awareness and education initiatives can also play a significant role in promoting sustainable practices and fostering respect for these magnificent creatures.
The declining population of great white sharks in South African waters due to the presence of killer whales and the specter of climate change poses a significant challenge for conservationists and the local economy alike. Efforts must be intensified to address these issues, preserve the delicate balance of the marine ecosystem, and protect these iconic apex predators for future generations. Only through collective action can we secure the future of great white sharks and maintain the allure of South Africa's marine wonders.